By: Tomás Rosada Villamar, Elena Mora López, and Hyemi Lee
The global agri-food system faces significant challenges, particularly from climate change. However, Mexico has demonstrated resilience, ranking 12th globally in food production and 9th in agri-food exports in 2022 (SIAP, 2023). Agriculture is vital for Mexico due to its historical and economic significance (SIAP, 2022), supporting local food security and small-scale producers. Consequently, Mexico is investing in enhancing agri-food system resilience and innovation through partnerships and knowledge exchange.
The concept of Smart Farming[1] has been explored recently. The goal of this project has been to learn, adapt, and adopt digital agriculture practices, leveraging on Korea’s expertise. Through "Strengthening Agriculture and Food Systems by Promoting Access to Finance Project (Agroincluye)" supported by the KGGTF grant, the project partner, Fideicomisos Instituidos en Relación con la Agricultura (FIRA) of Mexico, seeks to improve productivity and climate resilience. This initiative seeks to integrate smart farming technologies to enable sustainable national agri-food system and support climate-smart agricultural initiatives for inclusive green growth.

Under the Agroincluye project, the World Bank's Agriculture and Food Global Practice for Latin America and the Caribbean (SLCAG) has undertaken a comprehensive series of initiatives. These include a study tour to Korea, facilitating knowledge exchange and partnerships with Korean public and private sectors. Learning materials were developed for the World Bank's Open Learning Campus (OLC). Building on the lessons learned and partnerships established during the study tour, Korean experts in digital agriculture visited Mexico twice to assess the feasibility of applying smart farm technologies and design a tailored model to the Mexican context. These efforts leverage the KGGTF and Korea’s smart farming expertise to enhance Mexico’s agricultural sector.
Understanding the concept of smart farms in Korea
FIRA representatives, supported by KGGTF, visited Korea from June 20 to June 24, 2022, for a study tour on Korean smart farm technologies. The tour included policy exchanges, knowledge sharing, and site visits. FIRA engaged with Korean agricultural authorities, including the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) and the Rural Development Administration (RDA). Through this engagement, FIRA gained smart agriculture industry policies, support for young farmers, and advancements in smart agriculture systems. FIRA also shared their vision for adopting smart technologies and climate-smart systems, including piloting smart farm models in FIRA's Technology Development Centers (TDCs) and scaling them nationwide.

Additionally, six representative Korean startups in digital agriculture for crops and livestock participated in a training session on smart farm technologies. They showcased various innovations, including vertical farms with environmental controls and AI for yield forecasting, a data-driven agriculture platform for product sale and distribution, autonomous agricultural machines, integrated livestock systems, and digital animal healthcare. The session, followed by a networking event organized by Korea Agriculture Technology Promotion Agency (KOAT), emphasized the importance of these technologies.
Site visits to Gimje Innovation Valley, RDA's agriculture machinery testbed, and smart greenhouses demonstrated digital technologies' practical applications in horticulture and livestock. These visits highlighted the benefits of technology adoption, such as mitigating climate risks, boosting productivity, and improving rural working conditions.
Tomatoes and beef hold significant commercial value for export in Mexico (SADER, 2024). In light of this, a tomato smart farm and a calf smart farm have been selected. A visit to a tomato smart farm revealed potential advances in sustainable production, highlighting opportunities for enhanced yield and quality through protected agriculture and efficient cultivation practices.
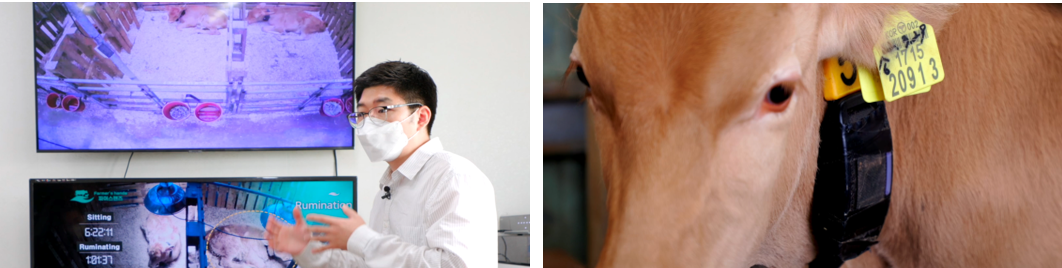
The cattle and dairy farms employing bio-signal and behavioral pattern analysis demonstrated how these technologies enhance calf health and growth monitoring, reducing mortality rates and improving breeding. Representatives emphasized tech's role in productivity, sustainability, and supporting young farmers, while stressing the need for government support in digitalization by providing financial access, technical assistance, and capacity building. These efforts align with FIRA's mission to assist local farmers in Mexico.
Toward a Climate-Smart Agri-Food System: Integrating Smart Farm Technologies in Mexico
Leveraging KGGTF support, Korean smart farm experts were dispatched to FIRA's TDCs in September 2023 and April 2024. Collaborating with counterparts, they assessed pilot greenhouses, developing scalable plans for technology adoption by small-scale farmers.
FIRA's TDCs lead climate-sustainable production, equipped with rainwater harvesting, recirculation systems, solar panels, and use of biofertilizers to reduce carbon emissions. FIRA fosters technology transfer to local farmers and connects traditional and innovative producers. This collaboration also extends to local University to enhance agricultural solutions.
Through these visits, Korean experts evaluated greenhouses at three pilot TDCs–Salvador Lira López, Villadiego, and Tezoyuca. They aimed to develop them into smart farms by adopting scalable technologies tailored to each facility. Their assessments identified areas for immediate improvement and provided guidance for digitalization and automation to facilitate technology adoption by Mexican farmers.

.................................................................................
[1] The concept of a Smart Farm, also known as digital agriculture, involves the integration of advanced information and communication technologies (ICT) such as Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, big data, drones, sensors, and data analytics into agricultural practices to improve efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of agricultural production. Smart Farms utilize real-time data and automation to optimize various processes including irrigation, fertilization, pest control, and livestock management (FAO, OECD, and IBM)
The grant, An agri-tech smart farm pilot for greening growth in Mexico’s post COVID-19 recovery, was approved in 2021, led by Tomas Ricardo Rosada Villamar, Senior Agriculture Specialist